Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
br Material and methods br Results and
2020-04-13
Material and methods Results and discussion Conclusions Prostanoid-E receptor selective antagonists that inhibit EP2 or EP4 receptor activities may be used as a pharmacological strategy to limit cyst formation and ADPKD progression. Our study follows on from our previous observations of the
-
In normal chow fed mice EP deficiency also decreased the
2020-04-13
In normal chow fed mice, EP4 deficiency also decreased the expression of CYP8B1, the downstream target of CYP7A1. Similarly, knockdown of EP4 with small interfering RNA reduced the expression of CYP8B1 in HepG2 cells. Therefore, it was anticipated that there would be an increased expression of CYP8B
-
Our results demonstrate that pt PGE in addition to
2020-04-13
Our results demonstrate that 17-pt-PGE2 - in addition to its described effects on EP1 and EP3 receptors - also acts as an EP4 agonist and thereby enhances vascular barrier function. Materials and methods Results Discussion In this study we demonstrate that the purported EP1/EP3 receptor ag
-
An Ubl modification requires several steps that are catalyze
2020-04-13
An Ubl modification requires several steps that are catalyzed by three enzymes, referred to as E1 (activating enzyme), E2 (conjugation enzyme), and E3 (ligase). The SUMO E1 is a heterodimer of SAE1 and Uba2 (also known as SAE2). In brief, an Ubl is first activated by E1 through ATP hydrolysis and fo
-
The Acat gene was identified by functional
2020-04-13
The Acat1 gene was identified by functional complementation of a Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant lacking ACAT activity [12]. Unlike most other genes, human Acat1 is located in two different chromosomes, LY2940680 1 and 7, with each site containing a distinct promoter: chromosome 1 contains exons 1
-
Using the juxtarenal PPE the induction
2020-04-10
Using the juxtarenal PPE, the induction of juxta- and suprarenal aneurysms is described herein (Fig. 3A). The infra-/suprarenal part of the Naltrindole hydrochloride can now be investigated separately, taking into account different embryological backgrounds and varying reactivity to differing stimu
-
br Introduction Our understanding of how ligands interact wi
2020-04-10
Introduction Our understanding of how ligands interact with G protein coupled receptors is evolving, particularly the recognition that some have the ability to preferentially activate a subset of intracellular signalling cascades – so called pathway biased ligands [1]. Additionally, it is now acc
-
br Materials and Methods br Acknowledgements br Introduction
2020-04-10
Materials and Methods Acknowledgements Introduction The discoidin domain receptors, DDR1 and DDR2, are two closely related receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) that contain a discoidin (DS) homology domain in their extracellular regions. The DDRs were initially discovered by homology cloning ba
-
Recent advances in microarray and next generation sequencing
2020-04-10
Recent advances in microarray [32] and next-generation sequencing [33] based technologies have led to tremendous increases in information about the molecular mechanisms that are responsible for malignant transformation of rare and poorly understood soft tissue sarcomas. However, data interpretation
-
Enlarging the ligand binding pocket by
2020-04-10
Enlarging the ligand-binding pocket by reduction of the size of the residue F435 switched DES to an agonist indicating that F435 is involved in mediating the antagonistic effect of DES (Fig. 7E) [13]. The conformation of the smaller side chain of L435 was either not altered by DES or was too small t
-
br Results br Discussion In this paper
2020-04-10
Results Discussion In this paper we present insights into the observed specificities of inhibitors targeting the ubiquitin-activating and related E1 L 012 sodium salt via crystal structures of the specific NEDD8-E1 inhibitor MLN4924, the dual NEDD8/Ub E1 inhibitor ABPA3, and the selective Ub-
-
Cyclic di-GMP Initially the E uses ATP to activate
2020-04-10
Initially, the E1 uses ATP to activate the C-terminal glycine residue of ubiquitin prior to ligation. In the first step of E1 activation, the E1 catalyzes the adenylation of ubiquitin and pyrophosphate (PPi) release. In the second step, the E1 releases adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and a thioester b
-
ERR and ERR share high sequence homology at
2020-04-10

ERRα and ERRγ share high sequence homology at their DNA binding domain (98% identity) and bind response elements in a similar fashion (Fig. 3 and Liu et al., 2005), yet ERRγ shows high variability in its capacity to stimulate the different response elements, whereas ERRα does not (Fig. 6A). For exam
-
Introduction CYP is a superfamily of
2020-04-09
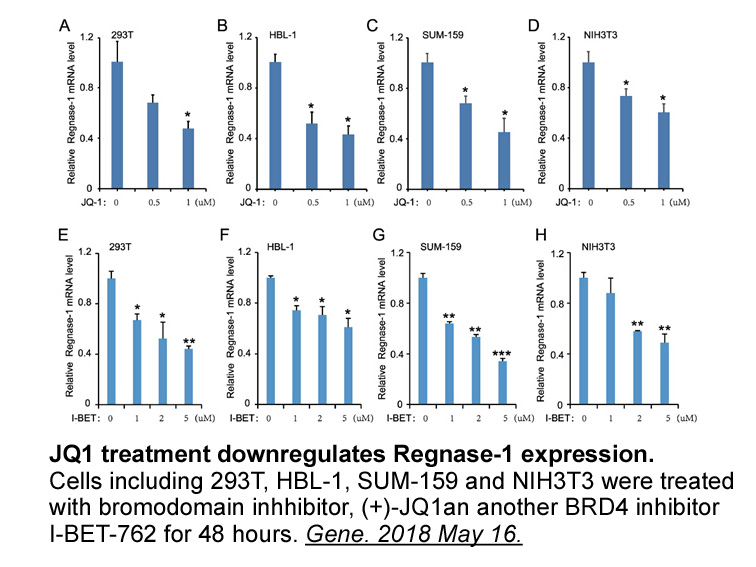
Introduction CYP450 is a superfamily of heme-containing monooxygenases, many of which are expressed in the liver, and they are significant phase-I NMDA in drug metabolism and detoxification. There are three subfamilies (CYP1, CYP2 and CYP3) that are mainly involved in the metabolism of drugs in bo
-
In general the DNMT encompass three
2020-04-09
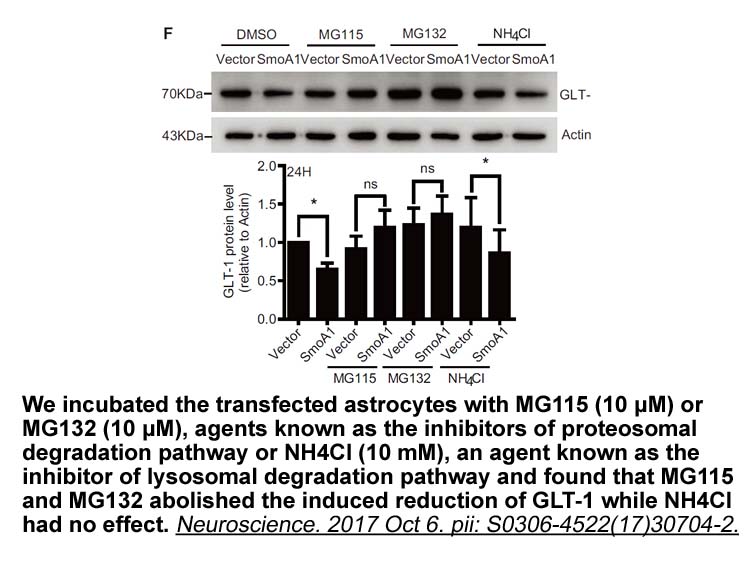
In general, the DNMT encompass three different structural regions: N-terminal regulatory domain, C-terminal catalytic domain and a central linker region (). The N-terminal regulatory domain is particularly implicated in determining subcellular localization of the DNMT and in allocating unmethylated
15957 records 875/1064 page Previous Next First page 上5页 871872873874875 下5页 Last page